How Meditation Works
Discover how meditation works, by focusing on the relaxation response.

Selfpause Affirmation App
Download the app to get 1,000’s of affirmation meditations and everything you need to write, record and listen to your own.
Meditation is an effective way to relax and clear your mind. The process involves focusing your mind on a specific object for some time. This is known as the Relaxation Response. Meditation can also influence cognitive skills and brain waves. The effects of meditation are profound, and they can significantly improve your life.
Relaxation Response

During meditation, the brain produces the relaxation response, a physiological process that causes blood pressure to fall and stress factors to decrease. This response can be induced by a variety of techniques, including progressive muscle relaxation, autogenic training, repetitive prayer, and meditation. The key is to maintain a focused mind while ignoring distracting thoughts.
A typical day can trigger a stress response several times, often for no apparent reason. Even non-life-threatening situations can trigger it. Over time, the release of stress hormones takes a toll on the body. Chronic stress results in increased heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle tension. However, the relaxation response may counteract these negative effects by slowing the breathing rate and reducing blood pressure.
Benson’s studies have found that meditation reduces stress levels and improves well-being. The benefits of meditation can be felt by the body at a deep level, and it has been proven to reduce anxiety and premenstrual symptoms. The authors report that the relaxation response can also help reduce chronic insomnia.
Different relaxation techniques can have different effects on different people. Practice different techniques until you find one that works best for you. While practicing meditation, try to remember that each person’s response to relaxation may be different. If you have a serious condition, talk with your doctor before trying a new technique. Some people experience severe symptoms after starting a relaxation technique.
Another way to elicit the relaxation response is through progressive muscle relaxation. This involves sequentially relaxing muscles from the toes up to the neck. Performing this exercise can take anywhere from 10 to 20 minutes. To practice progressive muscle relaxation, it’s best to find a quiet place with minimal distractions.
Effects of Meditation on Brain Waves
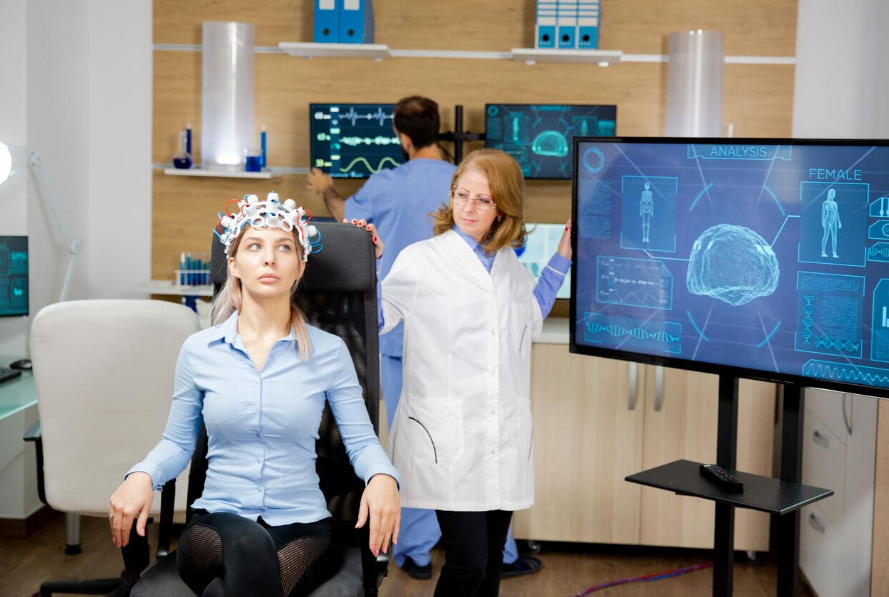
A recent study found that meditation can affect brain waves. The participants’ electroencephalographic (EEG) spectra varied by up to 24 percent. This effect was found across the entire frequency range, including the alpha and high-gamma bands. Interestingly, this effect was not found in the group of non-meditators.
Studies have shown that non-directive meditation produces fewer beta waves than direct meditation. While the two types of meditation are different, studies have found that both types of meditation improve overall relaxation and stress management. While non-directive meditation is not directly related to goal-oriented tasks, it results in more marked changes in electrical brain waves.
Meditation increases the power of the alpha and theta brain waves, which have been shown to improve brain health. In addition, meditation can make alpha brain waves the dominant ones. Studies have shown that it takes 40 days to make alpha brain waves dominate a person’s brain. This effect may be lifelong.
Meditation also leads to thicker brain tissue, particularly in the frontal areas. This extra gray matter increases mental stability and enables greater focus. In one study conducted at Harvard University, meditators had a thicker gray matter in areas of the brain linked to compassion and self-awareness. These areas are connected to the medial prefrontal cortex, which helps regulate anxiety and fear.
One popular method to study the state of meditation in meditating brains is functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), which uses a magnetic field to detect subtle changes in blood flow. Using this method, researchers can map brain activity with a high degree of accuracy and detail.
Effects of Meditation on Cognitive Skills

Meditation has been found to improve several cognitive skills, including attention and memory. This effect is beneficial for both adults and children. One recent study suggests that meditation improves verbal reasoning on standardized tests. The group receiving meditation training saw an increase of up to 16 percentile points in verbal reasoning, compared to those in the control group.
Other studies have demonstrated similar results. Meditation improves the functioning of the executive function, which is responsible for attention, working memory, awareness, and flexible thinking. Meditation triggers neurological changes that affect this region, such as a greater ability to focus on the present and avoid being emotionally affected by changes in focus. In addition, meditators show a greater ability to remain focused on a single object while listening to distracting sounds.
The study conducted by the University of California, Davis Center for Mind and Brain has examined the effects of meditation for seven years. The research team followed the practices of 60 experienced meditators at a mountain retreat center in Colorado. Participants received one hour of meditation each day. The group was evaluated before and after the retreat, and at six months. At the end of the seven-year study, 40 subjects were still practicing meditation for at least an hour a day.
During a meditation session, a certain protein in the brain is produced. This protein promotes the growth of new brain cells. This protein is known as a brain-derived neurotrophic factor. This protein is responsible for neuroplasticity, which means the brain can change to accommodate environmental conditions or respond to injury. During meditation, this process improves mood and well-being.
Effects of Mindfulness Meditation on People’s Lives

One recent study suggests that mindfulness meditation can improve the brain’s function and that it may even help reduce stress. It has also been linked to a lower risk of heart disease. In one study, participants who practiced mindfulness meditation had greater reductions in blood pressure than those who did not meditate.
During the meditation, participants may focus on their breathing, emotions, or mental images. They may also focus on the sensations of their bodies. A key to becoming more mindful is establishing an attitude of non-judgmental curiosity. In addition to practicing mindfulness, the practice may also reduce stress, improve overall health, or even improve relationships.
Nevertheless, research on the effects of meditation is still in its early stages. Some people experience unpleasant or distressing side effects, such as trouble sleeping. Some people may even experience recurrences of traumatic events and experiences. In this case, it’s important to consult with a trauma-informed therapist who can help guide you through the meditation process and develop coping mechanisms.
In one study, 96 people participated in three types of eight-week mindfulness meditation programs. These participants were middle-aged women who were seeking treatment for mild to moderate depression, stress, and anxiety. While some participants reported experiencing adverse effects, most reported that the meditation was beneficial and that the program helped them overcome the problem.
Several studies have looked at the relationship between mindfulness meditation practices and psychological well-being. One study found that mindfulness meditation practitioners reported higher levels of self-compassion and compassion than non-meditators. They also reported lower levels of psychological symptoms and thought suppression. The researchers concluded that these changes in cognitive and emotional well-being were related to the extent of meditation practice.
Adapting Meditation to Your Needs

First, you should find a place where you feel comfortable. Ideally, you should sit or lie down in a quiet place. You may also want to find a meditation partner or join a meditation class so you can get the proper guidance. If you feel alone, you can ask someone to sit or walk with you. This can help you to focus and improve your practice.
Another great benefit of meditation is its ability to alleviate depression and anxiety. It helps to decrease activity in the amygdala and pre-frontal cortex, which play important roles in the stress response. It also helps regulate hormones and blood circulation. It also promotes a peaceful mind and helps you sleep better.
There are many types of meditation, and you may want to experiment with them to find out what works best for you. There is no right or wrong way to practice meditation, and you may find it helpful in reducing stress and improving your health.
Our Top FAQ's
There are many potential benefits of meditation, including reduced stress and anxiety, improved focus and concentration, and increased feelings of calm and relaxation. These effects are thought to be related to changes in brain activity and the activation of certain neural pathways that are involved in regulating emotions and controlling the stress response.
Anyone can learn how to meditate, regardless of their age, background, or level of experience. Meditation is a skill that can be developed through practice and repetition, and there are many different techniques and approaches that can help individuals find a method that works best for them.
There are many different types of meditation, including mindfulness meditation, transcendental meditation, and loving-kindness meditation. These techniques can differ in their specific techniques, such as the use of mantras or visualization, as well as their intended effects, such as promoting relaxation or cultivating compassion.
Meditation is a practice that is often associated with spiritual and religious traditions, but it can also be secular and practiced independently of any specific belief system. Many different spiritual and religious traditions incorporate meditation as a way to cultivate mindfulness, concentration, and other mental and emotional states, but the practice can also be pursued for its own sake without any religious or spiritual context.
There are many common misconceptions about meditation, such as the idea that it is only for certain individuals or that it requires a special talent or ability. In reality, anyone can learn how to meditate and benefit from its effects, and there are many different approaches and techniques that can be tailored to individual needs and preferences. Other common misconceptions include the idea that meditation involves emptying the mind or achieving a state of total stillness, when in fact it often involves actively focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or sensation.
