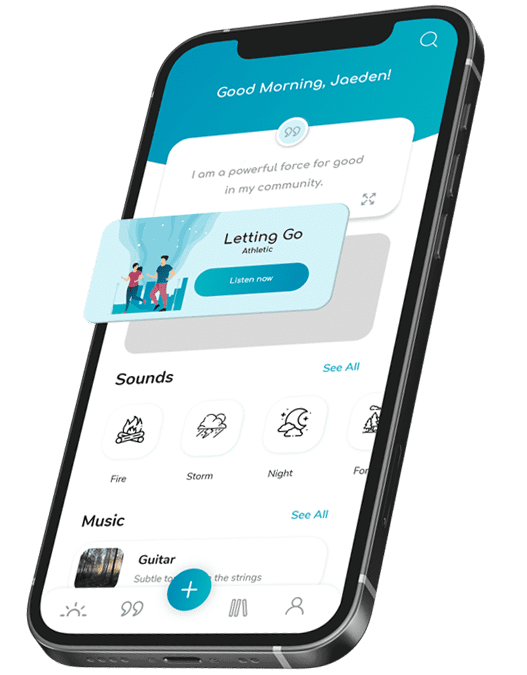
Start your affirmation journey with Selfpause Plus

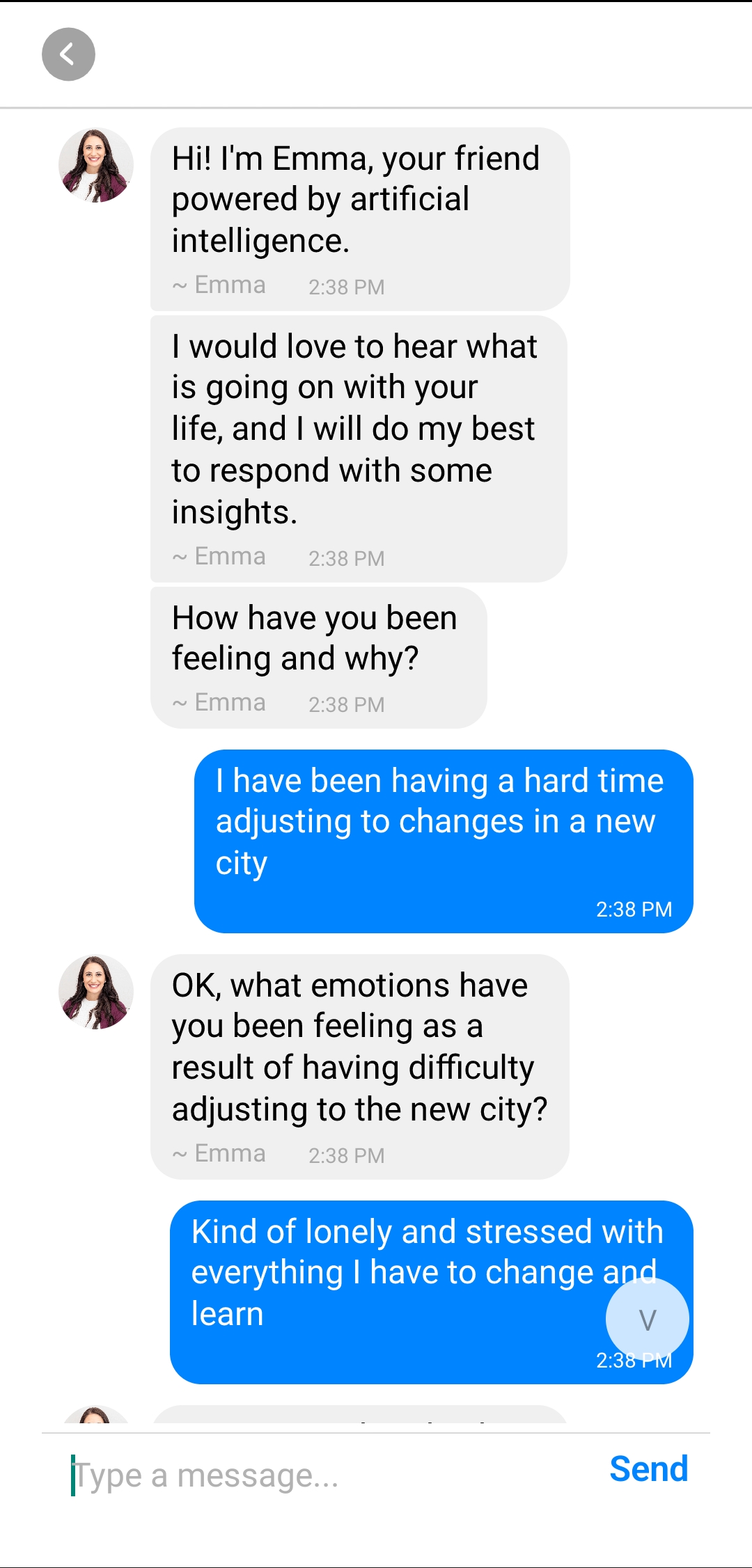
AI Life Coach Chat
An AI life coach in your pocket, anonymous, secure and available 24/7.

Self-Recorded Affirmations
Record unlimited personalized affirmations that are backed up to the cloud.

Guided Affirmations
Listen to 1,000's of affirmations in our guided affirmation sessions.

Ambient Sounds & Music
Get the full library of ambient sounds and music to layer with your affirmations.
Listen to new affirmation sessions for every area of your life.

Millionaire Mindset

Manifesting Success

Athletic Mindset

Childrens Confidence
“I’m so glad I discovered Selfpause. I’m always working to help athletes elevate their game… these affirmations help.”
– Troy Polamalu, 2020 Pro Football Hall of Fame


Create and record your own personalized affirmations
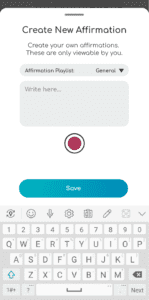
Write
Create and write your own personal affirmations
Record
Record your affirmations in your own voice
Layer
Layer ambient sounds and music in the backgound
Visualize
Listen to and visualize your affirmations in action
★★★★★ Rated 5 out of 5
Hear how Selfpause is changing lives
I’ve always believed in the power of positive affirmations, but as a beginner, I feel self-conscious and awkward about saying things to myself in a mirror every morning. But listening to these affirmations is SO AWESOME! It doesn’t feel unnatural, it’s amazing how quickly I can feel myself calm down amidst high stress, and the prerecorded affirmations are very powerful to me.
Using this app has become such a crucial part of my routine. It’s perfect for people who are new to affirmations like me, and I was surprised to realize how effectively it helps me get into a good mindset to start the day & work toward my goals. The app itself is beautifully designed and makes it easy for me to select affirmations based on my what I’m wanting to focus on in the moment.
Okay- if you have issues with negative self talk, this app is for you! I put it on favorites and listen for 30 minutes while getting ready for the day. This is a great way to bombard myself with positive thoughts and ideas! I love it! I downloaded this app also because I’m reading about the benefits of affirmations and the incredible power of the brain.
Love this app! Such well thought out and high quality affirmations. They have a female voice and a male voice and they have awesome accents. I’ve been needing an app like this for SO long, I love to meditate but having positive affirmations to meditate with really makes it so much more meaningful and brings it to a whole new level.
Unlock Selfpause Premium
Selfpause Premium
$
59
99 /yr
-
Empower yourself with an AI Life Coach
-
100+ guided affirmations
-
Entire library of soothing background sounds, music, and binaural beats
-
Back up your personal library to get your affirmations on any device
-
Create unlimited recordings
-
Become a supporter and help us offer positivity to those who need it most
Free in the app
$
0
-
guided affirmation sessions
-
daily affirmation notifications
-
record your own affirmations